How the System Thinks
Australia does not evaluate doctors emotionally or subjectively. It looks at equivalence.
- Where did you train?
- Who assessed you?
- How recently did you practise?
Those three factors shape everything that follows. Nationality does not matter. Seniority alone does not matter. What matters is whether your previous assessment framework aligns with Australian expectations.
This is why two doctors with the same number of years in practice can face completely different pathways.
When Australia Accepts Prior Assessment
Some doctors already come from systems Australia trusts. This is the reason the Competent Authority pathway exists.
If you trained or gained registration in countries such as the UK, Ireland, the US, Canada, or New Zealand, Australia will accept that your clinical knowledge and skills have already been assessed to a comparable standard.
Doctors who meet both the assessment and experience requirements can apply for provisional registration without sitting the AMC exams. They still go through verification and supervision, but they do not repeat assessments unnecessarily.
After securing a suitable role, they complete twelve months of supervised practice. Once that year ends, they can apply for general registration and continue working as a GP.
When AMC Part I and Part II Become a Part of the Journey
Many international doctors do not fall under a recognised competent authority. This does not imply weaker training. It reflects differences in how countries test readiness for independent practice.
In these cases, Australia uses the Australian Medical Council (AMC) Part I exam to assess applied competence. The exams do not reward theoretical depth alone. They reward clinical prioritisation, safe decision-making, and contextual judgment.
The Importance of Clinical Practice & Mock Exams to Clear AMC
There is a pattern among candidates who fail repeatedly. They read constantly but rarely test themselves clinically.
AMC Part II exam (Clinical assessment) punishes hesitation and rewards clarity. Candidates who try to be exhaustive often perform worse than those who are decisive and safe.
A structured AI-based mock series exposes these tendencies early. AI-based mock exams show how time pressure changes judgment and where reasoning breaks down. This insight rarely comes from books alone. Doctors who treat mock exams as feedback rather than judgment usually adapt faster.
First Job, Then Registration
Provisional registration does not come first. Employment does. Doctors must secure an approved position before applying for provisional registration. That role must include supervision that meets regulatory standards.
The Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA) oversees this process. English language requirements, recency of practice, and professional conduct apply to every IMG, regardless of pathway.
AHPRA publishes all requirements directly, and those pages should always be the primary reference.
Doctors who align job searches with registration timelines avoid months of unnecessary waiting. Jobslly aligns your skills and experience with verified job opportunities. Apply for the best suitable job and carve a successful healthcare career.
The PESCI Pathway
For doctors entering general practice, another step often applies before provisional registration. This step is called the Pre-Employment Structured Clinical Interview, commonly referred to as PESCI.
PESCI is is a structured interview designed to assess whether an international doctor is suitable for a specific general practice role in Australia. The assessment focuses on clinical judgment, communication, and readiness to work safely within the Australian primary care system.
Most IMG doctors applying for GP roles under the Competent Authority or AMC pathways must complete PESCI unless they qualify for an exemption. The interview relates to a nominated position, not to general eligibility, which means doctors must secure a job offer before undergoing PESCI.
An approved college (mostly Go8) or assessment body conducts the interview and evaluates the doctor’s suitability for that particular practice setting.
Is PESCI Important for GP?
A positive PESCI outcome allows the Medical Board to consider the application for provisional registration with approved supervision arrangements.
Doctors often underestimate PESCI and prepare too late. In practice, PESCI failures usually result from unfamiliarity with Australian primary care expectations rather than gaps in medical knowledge. Understanding local referral systems, escalation protocols, and patient-centred communication plays a significant role in the outcome.
Once PESCI and supervision arrangements are approved, the registration process can move forward without further procedural delays.
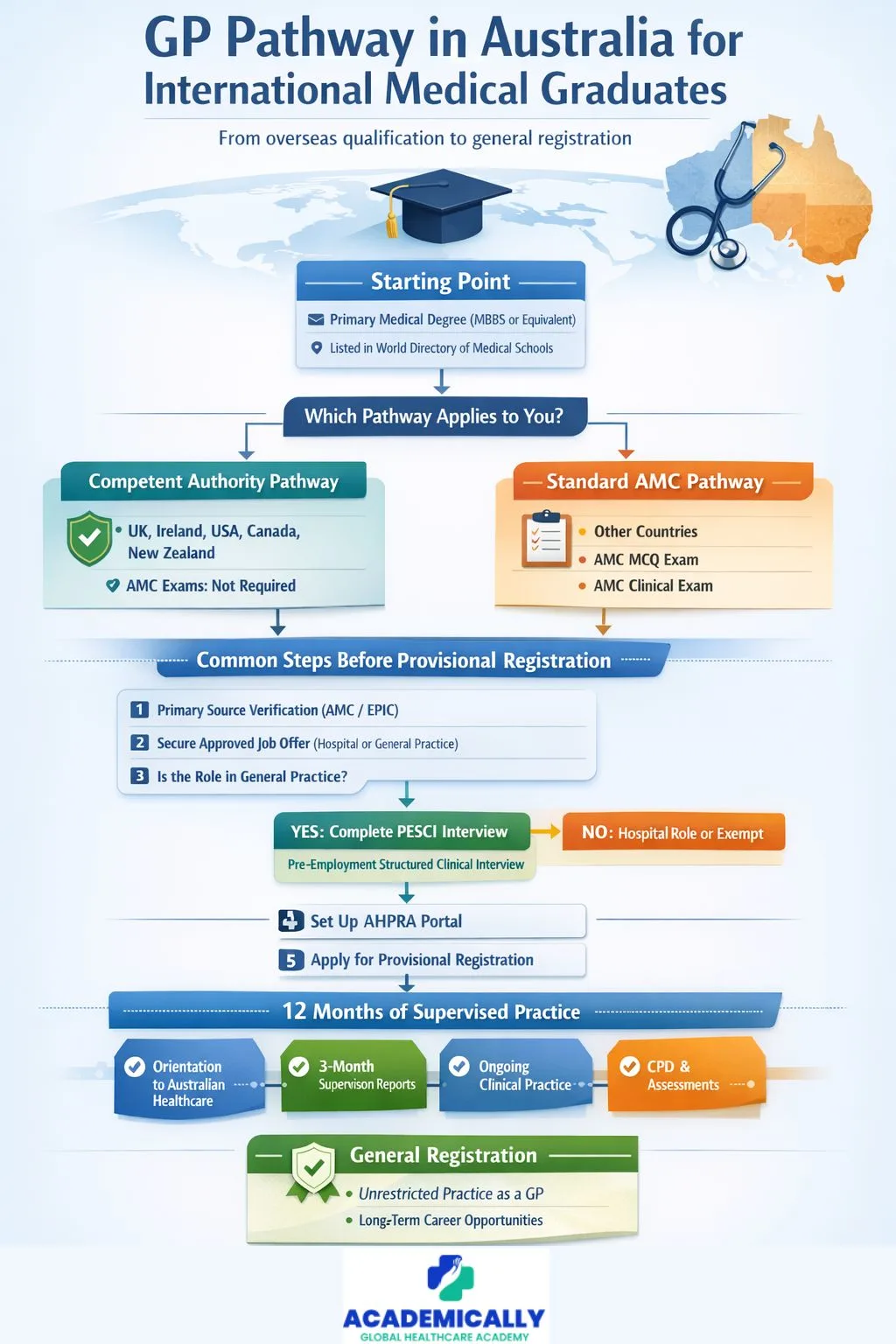
Supervised Practice
Supervised practice is not symbolic. It is practical.
This is where international doctors learn how referrals work, how shared care functions, how documentation protects clinicians, and how accountability operates day to day in Australia.
Doctors who treat this year seriously settle faster and feel more confident once restrictions lift.
General Registration and What Comes After
After 12 months of supervised practice, eligible doctors apply for general registration. This step removes conditions and allows unrestricted practice.
For most IMGs, this moment feels less dramatic than expected. It simply feels stable. Planning becomes long-term. Careers stop feeling provisional.
From here, doctors may pursue GP fellowship pathways, longer contracts, or permanent settlement options.
Closing Thoughts
Australia’s GP pathway does not reward urgency. It rewards accuracy.
International doctors who take the time to understand where they fit, choose the correct route, and prepare with purpose usually find the system fair, even if demanding.
For those willing to approach it methodically, becoming a GP in Australia remains not only achievable but also professionally fulfilling and sustainable.





