What are ACE Inhibitors?
These are types of drugs that work by widening blood vessels to ease the heart from pumping blood. They are mainly used to manage the following conditions:
- Hypertension (High blood pressure): Because of the ability of ACE inhibitors to lower blood pressure, the chances of stroke, heart attack, and kidney problems are minimised.
- Heart Failure: They enhance the pumping of blood from the heart which alleviates the discomforts relating to heart failure and increases chances of survival.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): This is common especially among diabetic patients. It involves the use of ACE inhibitors to decrease the intra kidney pressure and thus protect from deterioration of kidney function.
- After Heart Attack: They can increase chances of surviving and lower the chances of experiencing heart problems again, post a heart attack.
How Do ACE Inhibitors Work?
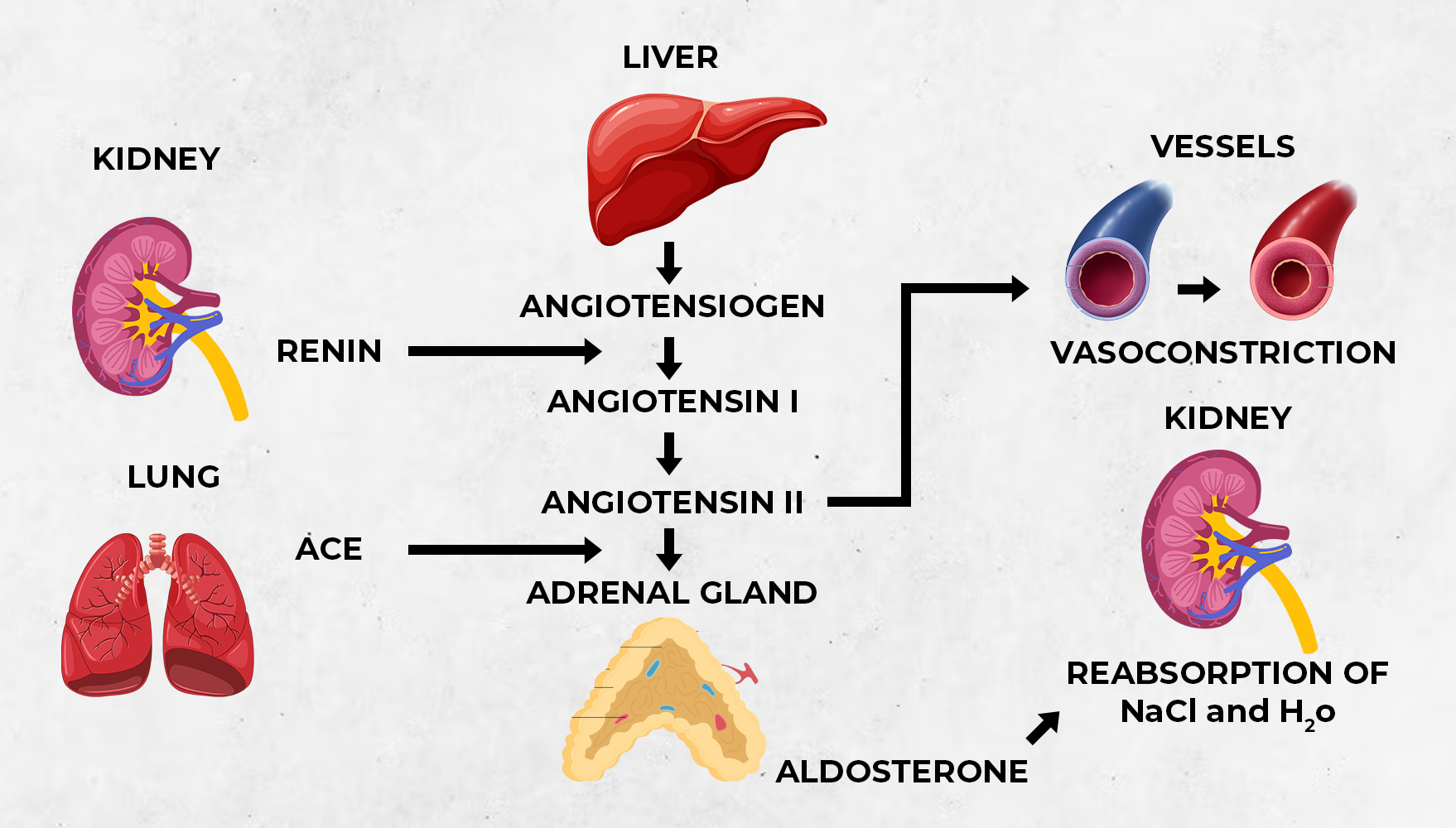
ACE inhibitors work by blocking the activity of an enzyme called angiotensin-converting enzyme. This enzyme plays an important role in the body’s renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which regulates blood pressure.
Here’s how it works:
- Blocking Angiotensin II Production: ACE inhibitors prevent the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a vasoconstrictor. Angiotensin II narrows blood vessels and increases blood pressure. By reducing its production, ACE inhibitors help blood vessels stay relaxed and open.
- Lowering Blood Pressure: With blood vessels more relaxed, blood flows more easily, and blood pressure decreases, reducing the workload on the heart.
- Reducing Aldosterone Secretion: ACE inhibitors also lower the production of aldosterone, a hormone that causes the kidneys to retain sodium and water. By decreasing aldosterone levels, ACE inhibitors help reduce fluid retention, further lowering blood pressure.
Commonly Used ACE Inhibitors
Several ACE inhibitors are available on the market, and they are often prescribed based on the specific needs of the patient. Some commonly prescribed ACE inhibitors include:
- Lisinopril
- Enalapril
- Ramipril
- Benazepril
- Captopril
- Quinapril
- Fosinopril
- Perindopril
Benefits of ACE Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors offer several significant benefits, particularly for patients with hypertension, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease:
- Blood Pressure Control: ACE inhibitors are highly effective at lowering blood pressure, which is critical for preventing complications such as heart attacks, strokes, and kidney damage.
- Heart Protection: For people with heart failure or those recovering from a heart attack, ACE inhibitors can improve heart function and increase survival rates.
- Kidney Protection: ACE inhibitors are particularly beneficial for patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease, as they help protect the kidneys by reducing pressure within the kidneys' filtering system.
Side Effects of ACE Inhibitors
Like all medications, ACE inhibitors can cause side effects. Some of the common side effects include:
- Cough
- Elevated Blood Potassium Levels (Hyperkalemia)
- Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
- Kidney Function Changes
- Angioedema
Who Should Avoid ACE Inhibitors?
ACE inhibitors are not suitable for everyone. They should be used with caution or avoided in the following situations:
- Pregnancy: ACE inhibitors can cause birth defects if taken during pregnancy, particularly in the second and third trimesters. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should avoid these medications.
- Allergy or Intolerance: If you have experienced angioedema or severe allergic reactions to ACE inhibitors, you should not take them.
- Severe Kidney Disease: Patients with advanced kidney disease may need alternative treatments, as ACE inhibitors can sometimes worsen kidney function.
Conclusion
ACE inhibitors are key players in treating high blood pressure, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease. They help lower blood pressure, protect the heart, and slow down kidney damage, making them incredibly valuable for managing these conditions. But, like any medication, it’s important to use them with the guidance of a healthcare provider to ensure they’re safe and effective for you.
For more easy-to-understand information on ACE inhibitors and other important medications, check out Academically’s Blogs. We’re here to help you stay informed and confident in your healthcare journey with the latest updates in the healthcare world.



