Classification
The classification of antiemetic agents includes different classes of drugs, each targeting different mechanisms. Here’s the classification of antiemetic drugs.
1. Anticholinergics: Scopolamine (hyoscine), dicyclomine.
2. Antihistamines (H-blockers): Dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, cyclizine, meclizine, hydroxyzine, promethazine, doxylamine, cinnarizine.
3. 5-HT3-receptor antagonists: Ondansetron, granisetron, dolasetron, palonosetron.
4. Prokinetic agents: Metoclopramide, domperidone.
5. Neuroleptics: Chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, prochlorperazine, haloperidol.
6. Cannabinoids: Dronabinol.
7. Adjuvant antiemetics
(a) Glucocorticoids: Betamethasone, dexamethasone, methylprednisolone.
(b) Benzodiazepines: Lorazepam, alprazolam.
Uses and side effects
| Drugs | Uses | Side-effects |
| Anticholinergics | Motion sickness | Sedation, dryness of mouth, blurred vision and urinary retention |
| Antihistamines | Motion sickness, morning sickness, Meniere’s disease, drug-induced, post-operative, radiation sickness and cancer chemotherapy-induced vomiting | Drowsiness and dryness of mouth |
| 5-HT3-receptor antagonists | Cancer chemotherapy-induced vomiting, radiation sickness and post-operative vomiting | Headache, dizziness and diarrhea |
Prokinetic drugs
|
|
|
| Neuroleptics | Drug-induced, disease-induced, post-operative, cancer chemotherapy and radiation-induced vomiting | Extrapyramidal symptoms, sedation, dystonic reactions and orthostatic hypotension |
| Dronabinol | Vomiting due to cytotoxic drugs and radiation sickness | Sedation, dysphoria, hallucinations and drug dependence |
| Glucocorticoids (Adjuvant antiemetics) | Adjuvant antiemetic along with ondansetron or metoclopramide in cancer chemotherapy-induced vomiting | Metabolic disturbances |
| Benzodiazepines (Adjuvant antiemetics) | Psychogenic and anticipatory vomiting | Sedation and drowsiness |
Mechanism of Action
Here are the mechanisms of action of various antiemetics:
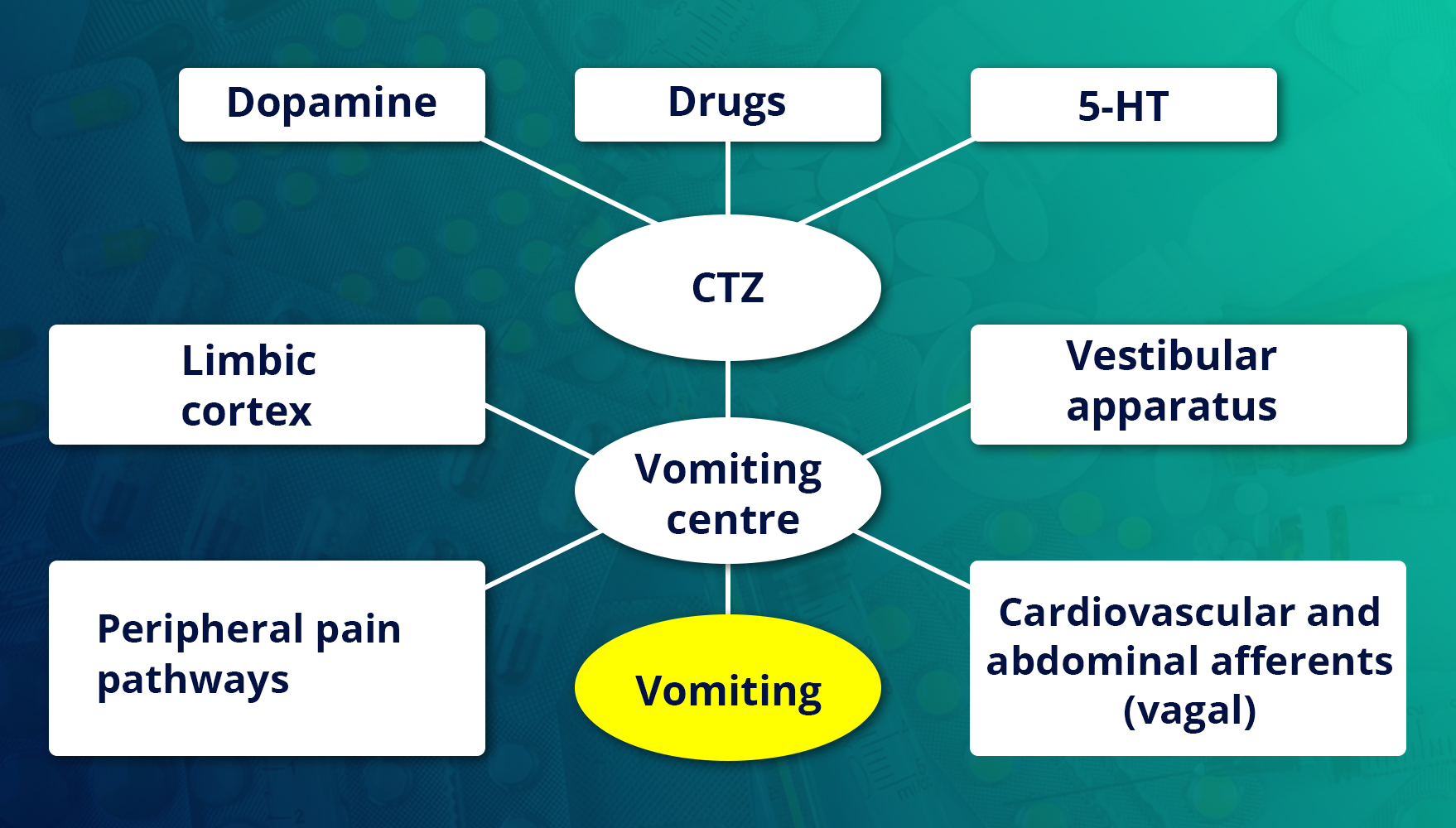
Anticholinergics
Scopolamine is the drug of choice to prevent motion sickness. If it blocks afferent impulses from the vestibular apparatus to the vomiting centre by its anticholinergic action. Its selective effect also contributes to its antiemetic effect.
Antihistamines H1 blockers
H1 blockers are mainly useful for the prevention of motion sickness. They are also effective in morning sickness, postoperative and other types of vomiting. Their antiemetic effect is due to sedative and central anticholinergic actions.
5-HT3- Receptor Antagonists
Their antiemetic effect is due to the blockade of 5-HT3- receptors on vagal afferents in the gut. In addition, they also block 5-HT3-receptors in the CTZ and solitary tract nucleus (STN).
Prokinetic drugs
Drugs that promote coordinated movement of upper GIT and hasten gastric emptying are called prokinetic drugs.
Neuroleptics
They are potent antiemetics. Their antiemetic effect is due to the blockade of D2-receptors in the CTZ. In addition, they have anticholinergic and antihistaminic actions. Among these, prochlorperazine is commonly used as an antiemetic. They are effective in the treatment of vomiting due to drugs, uraemia and systemic infections. These drugs are not used for morning sickness. Neuroleptics are not as effective as ondansetron and metoclopramide in cytotoxic drug-induced vomiting and radiation sickness. They are less effective in motion sickness.
Cannabinoids
Dronabinol
It is the principal psychoactive component of marijuana and is used to prevent cancer chemotherapy- induced vomiting from responding to other antiemetics. It is effective orally. It produces serious side effects, such as sedation, hallucinations, disorientation, tachycardia, palpitation, increased appetite and drug dependence-hence kept as a reserve antiemetic.
Adjuvant Antiemetics
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids, such as dexamethasone, betamethasone and methylprednisolone, are used as adjuvant antiemetics. These agents are commonly used in combination with ondansetron or metoclopramide in the treatment of anticancer drug-induced vomiting. The beneficial effect of steroids is due to their anti-inflammatory property and inhibition of prostaglandin (PG) synthesis.
Benzodiazepines
Lorazepam and alprazolam are used to control psychogenic and anticipatory vomiting. The beneficial effect is mainly due to their sedative, amnesic and anti anxiety effects.

Final Thoughts
Antiemetics are essential in managing nausea and vomiting, offering significant relief for symptoms due to various causes.
By understanding the different types of antiemetics, their specific uses, and potential side effects, pharmacists and other healthcare providers can better understand the treatment options.
Antiemetics is one of the topics for the KAPS Exam and other healthcare professional exams. Being thorough in this topic will help you ace the KAPS exam with ease.
For first-class preparation for the KAPS Exam, join Academically’s KAPS Exam Preparation Course. You will get access to all the study materials, tips and tricks to solve the MCQs easily, personalised guidance, and more.
Please fill out this form today for a one-on-one counselling session with our expert.





