Why Astropharmacy in Space?
In space missions with limited space and weight, carrying all necessary pharmaceuticals is impractical. This is where astropharmacy comes in, allowing for the on-demand production of protein drugs using genes as templates for cellular or cell-free expression of proteins.
Space presents unique health challenges like bone and muscle deterioration, kidney stones, and fluid redistribution. Protein-based drugs offer potential treatments for these issues, making astropharmacy crucial for space health.
Here's how an astro-pharmacist can create instant biopharmaceuticals in space: Cells produce specific drugs, such as teriparatide for osteoporosis or G-CSF for stimulating white blood cell production. This process involves three essential steps:
- Designing paper-based microfluidic devices that use fusion proteins for diagnosis.
- Utilising cellular or cell-free systems for drug manufacturing. Cellular systems use bacteria like Vibrio natriegens (Vmax) or Bacillus subtilis, which can be stored for years without refrigeration. Alternatively, a cell-free system operates outside the constraints of a living cell, allowing high protein yields.
- Purifying the synthesised drugs on a microfluidic chip can be automated for future use with minimal training.
This streamlined approach to drug synthesis and purification within an astropharmacy ensures that astronauts can access vital medications without the limitations of shelf-life and storage, particularly crucial for long-duration space flights.
Health Problems in Space
Space exploration poses unique health challenges for astronauts, especially during long missions beyond low-earth orbit. Here are some of the main issues reported during missions to the International Space Station (ISS) and Space Shuttle missions from 1988 to 1995:
Zero-G Sickness: Astronauts can feel nauseous and unwell due to the brain's struggle to adjust to zero gravity, similar to motion sickness.
Mental Health: Being confined in a small space for a long time can affect astronauts' mental well-being, potentially impacting mission success.
Muscle Weakness: Prolonged space travel leads to muscle weakness, which can be mitigated through regular exercise using dedicated gym equipment onboard spacecraft.
Visual Deterioration: Spending months in space can cause changes in eye structure, affecting vision and depth perception.
Bone Problems: Weightlessness can weaken bones, posing risks to astronauts' bone health.
Head Congestion: Fluid shifts in zero gravity can cause fluid to accumulate in astronauts' heads, leading to puffy faces.
Decreased Immune System Efficiency: Spaceflight stressors can weaken the immune system, making astronauts more sensitive to illnesses.
Radiation Hazards: Astronauts are exposed to harmful radiation types outside Earth's protective magnetic field, which can affect their health.
Medical Emergencies: Space missions can have emergencies like trauma or injuries requiring specialised care onboard.
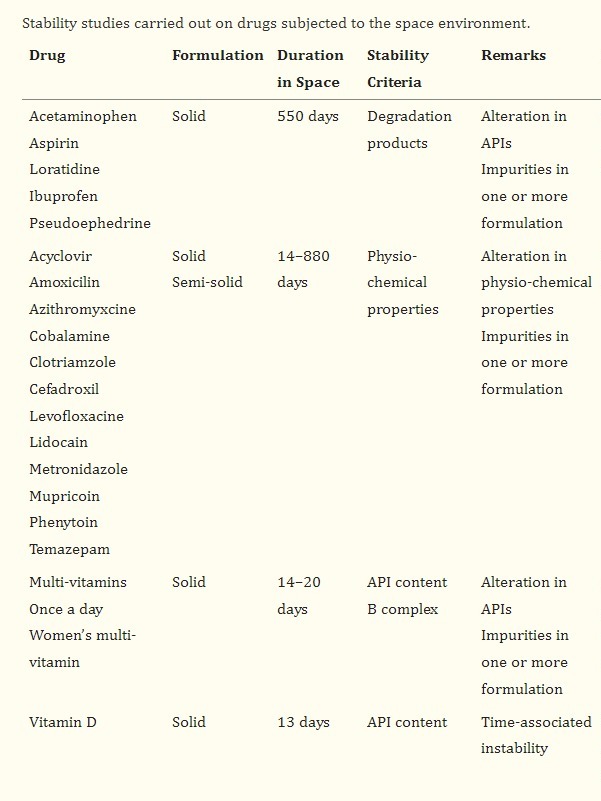
Pharmaceutical Product Stability in Space
Ensuring the stability of medications in space is crucial for astronauts' health during long missions. Space radiation can degrade drugs, affecting their potency and safety. Both liquid and solid formulations are vulnerable to degradation. To ensure effectiveness, medications must be tested for changes in physical and chemical properties after exposure to space conditions. Limited research has been conducted on this topic, highlighting the need for further study to ensure the safe use of medications in space.
Pharmacogenomics and Space
Pharmacogenomics, which studies how genes influence a person's response to medication, offers a personalised approach to drug therapy. While this method advances on Earth, its application in space is limited. However, integrating pharmacogenomics into space medicine could optimise drug effectiveness while minimising adverse events for astronauts.
There is little research on how genetics contribute to medication variability in space. Factors like environmental changes during launch and return to Earth, as well as variations in nutrition and fitness, can affect drug responses. Additionally, astronauts come from diverse ethnicities, genders, and ages, complicating medication dosing.
Despite these challenges, it is crucial to gather pharmacogenetic data and study its impact on drug outcomes in space. This will enable tailored drug therapy for astronauts, enhancing their health and well-being during space missions. As space exploration continues, understanding pharmacogenomics in the context of space medicine will become increasingly important for optimising astronaut health.
The Role of Pharmacists in Space
While the role of space medicine doctors is well-established, pharmacists' contribution to the health of space participants is often overlooked. However, pharmacists are crucial in ensuring the safe and effective use of medications in space missions. Here are some major role of pharmacists in space:
Category | Role |
| Evolution of the medical domain |
|
| Patient care |
|
| Compounding |
|
| Dispensing |
|
| Clinical pharmacokinetics monitoring |
|
| Pharmacy integration |
|
| Clinical pharmacogenomics |
|
| Pharmacovigilance |
|
| Drug information |
|
| Commercial space travel |
|
In Summary
This highlights the challenges related to pharmaceutical stability in microgravity conditions during space missions. It also discusses how deep space exploration can affect human physiology and pharmacogenetics, leading to changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (PK-PD).
Pharmacists are crucial in ensuring medication safety and effectiveness in space missions. They must continue to research and develop strategies to overcome challenges related to pharmaceutical stability in space, considering factors like space radiation and microgravity.
Furthermore, as space travel becomes more accessible to civilians with initiatives like SpaceX's Crew Dragon, the need for pharmacists to understand the unique health considerations of space travellers becomes increasingly important. By studying this subject more deeply, pharmacists can contribute to the success and safety of future space exploration missions, whether they involve professional astronauts or private citizens.
Fill up this form for a free one on one counselling session.

